Painful Sex
If you are having sexual pain don’t dismiss it as something “in your head” as it can be very real. As more than 30% of women reported pain during their last sexual encounter. There are many causes of sexual pain including: lack of lubrication, stress, genital fit, genital infections, irritable bowel syndrome, endometriosis and menopause. It is best to discuss your sexual pain with your doctor so they may provide the treatment options that may help.

Libido
The libido or sex drive as it is more often referred to, is a person’s overall drive or desire for sexual activity. It is influenced by biological, psychological and social factors. The libido can be affected by many factors such as medical conditions, medications, lifestyle, relationship issues and age.
Sexual desires are an important factor in the formation and maintenance of an intimate relationship in both men and women. If there are changes in your sexual desire it is advised to have a discussion with your physician.

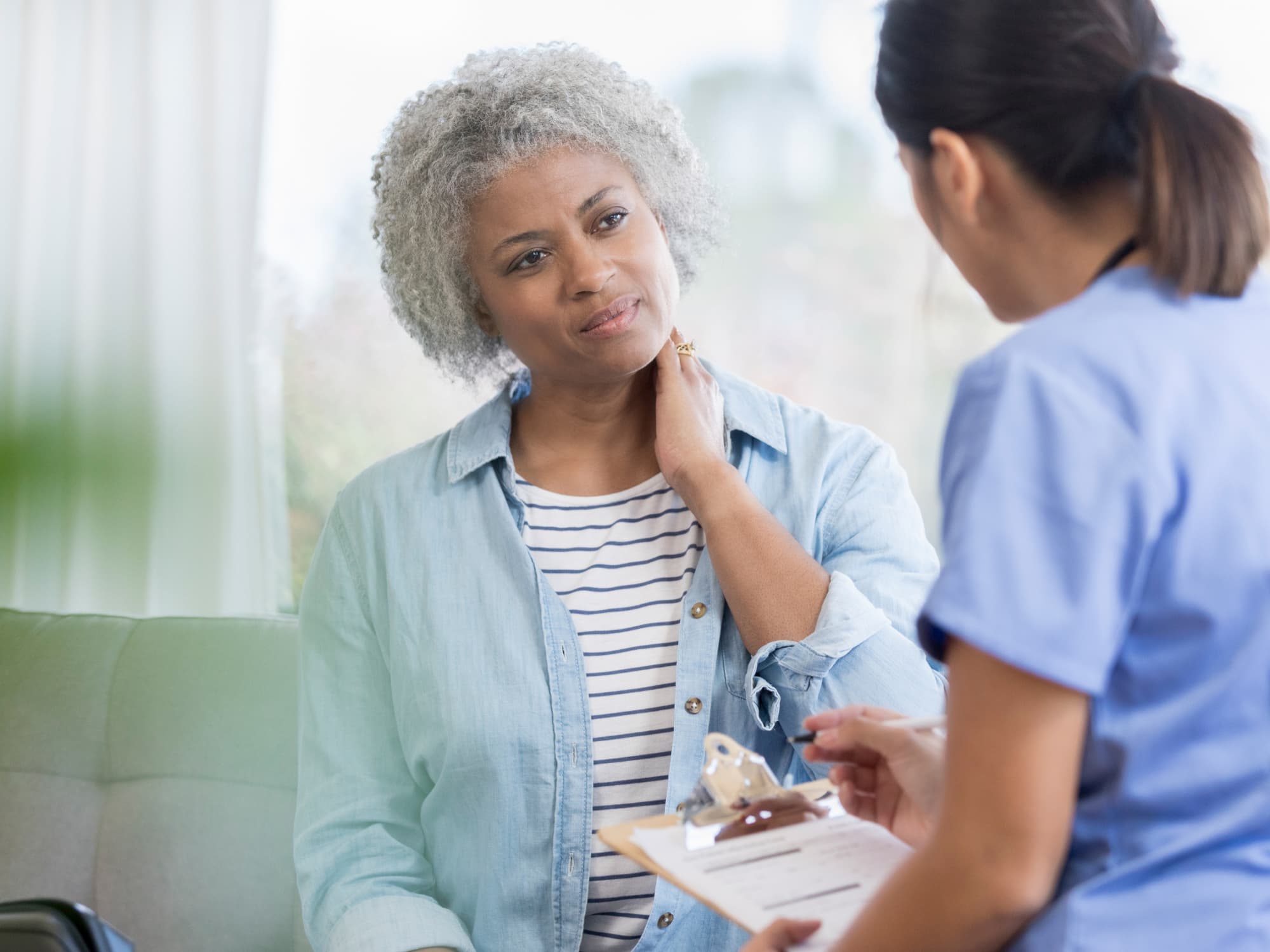
Painful Sex
If you are having sexual pain don’t dismiss it as something “in your head” as it can be very real. As more than 30% of women reported pain during their last sexual encounter. There are many causes of sexual pain including: lack of lubrication, stress, genital fit, genital infections, irritable bowel syndrome, endometriosis and menopause. It is best to discuss your sexual pain with your doctor so they may provide the treatment options that may help.
Vaginal Dryness
Normally, the walls of the vagina stay lubricated with a thin layer of clear fluid. Estrogen helps to maintain this fluid and keep the lining of the vagina thick and elastic. When there is a drop in the estrogen it reduces the amount of moisture and may also make the vagina thinner and less elastic. It can lead to itching, burning and painful intercourse. This is called vaginal atrophy.
The estrogen level can drop from: menopause, childbirth and breastfeeding, radiation or chemotherapy treatment for cancer, surgical removal of the ovaries, anti-estrogen medications, douching, certain allergy or cold medications and antidepressants. Your doctor will discuss your situation and may do a pelvic exam to rule out other possible causes for your discomfort.
Sexually Transmitted Infections

- Any woman can get BV.
- Some women with BV don’t know they have it because they have no symptoms.
- Women who have never had sexual intercourse may also be affected by BV, and it is common in pregnant women.
- Having BV can increase a woman’s susceptibility to other STDs. Pregnant women may deliver premature or low birth-weight babies.
- Most people who have chlamydia don’t know it since the disease often has no symptoms.
- Chlamydia is the most commonly reported STD in the United States.
- Sexually active females 25 years old and younger need testing every year.
- Easy to cure, chlamydia can impact a woman’s ability to have children if left untreated.
- Anyone who is sexually active can get gonorrhea.
- If they occur, symptoms in men and women vary depending on what part of the body is infected: Gonorrhea can affect the anus, eyes, mouth, genitals, or throat.
- This disease can impact a woman’s ability to have children if left untreated.
Genital human papillomavirus (also called HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are more than 40 HPV types that can infect the genital areas of males and females. These HPV types can also infect the mouth and throat. Most people who become infected with HPV do not even know they have it.HPV is not the same as herpes or HIV (the virus that causes AIDS). These are all viruses that can be passed on during sex, but they cause different symptoms and health problems.
- Genital herpes is a common STD, and most people with genital herpes infection do not know they have it.
- You can get genital herpes even if your partner shows no signs of the infection.
- If you have any symptoms (like a sore on your genitals, especially one that periodically recurs) laboratory tests can help determine if you have genital herpes.
- There is no cure for herpes, but treatment is available to reduce symptoms and decrease the risk of transmission to a partner.
- PID can lead to serious consequences including infertility.
- PID occurs when certain bacteria, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, move upward from a woman’s vagina or cervix (opening to the uterus) into her reproductive organs.
- Women can protect themselves from PID by taking action to prevent STDs or by getting early treatment if they have any genital symptoms such as vaginal discharge, burning during urination, abdominal or pelvic pain, pain during sexual intercourse, or bleeding between menstrual cycles.
- Prompt and appropriate treatment of PID can help prevent complications, including permanent damage to female reproductive organs.
In the United States, almost half of all persons with hepatitis A report having no risk factor for the disease. Among adults with identified risk factors, most cases occur among international travelers, household or sexual contacts, nonhousehold contacts (e.g., those encountered through play and daycare), and IDUs (437). Because transmission of HAV during sexual activity probably results from fecal-oral contact, measures typically used to prevent the transmission of other STDs (e.g., use of condoms) do not prevent HAV transmission. In addition, efforts to promote good personal hygiene have not been successful in interrupting outbreaks of hepatitis A. Vaccination is the most effective means of preventing HAV transmission among persons at risk for infection (e.g., MSM, illegal drug users, and persons with CLD), many of whom might seek services in STD clinics.
- HBV infection can be self-limited or chronic. In adults, only approximately half of newly acquired HBV infections are symptomatic, and approximately 1% of reported cases result in acute liver failure and death. Risk for chronic infection is inversely related to age at acquisition; approximately 90% of infected infants and 30% of infected children aged less than 5 years become chronically infected, compared with 2%–6% of persons who become infected as adults. Among persons with chronic HBV infection, the risk for premature death from cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is 15%–25%.
- HBV is efficiently transmitted by percutaneous or mucous membrane exposure to blood or body fluids that contain blood. The primary risk factors associated with infection among adolescents and adults are unprotected sex with an infected partner, unprotected sex with more than one partner, MSM, history of other STDs, and illegal injection-drug use.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States; an estimated 3.2 million persons are chronically infected. Although HCV is not efficiently transmitted sexually, persons at risk for infection through injection-drug use might seek care in STD treatment facilities, HIV counseling and testing facilities, correctional facilities, drug treatment facilities, and other public health settings where STD and HIV prevention and control services are available.
- Syphilis is easy to cure in its early stages.
- Signs and symptoms of syphilis include a firm, round, small, and painless sore on the genitals, anus, or mouth, or a rash on the body, especially on the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet.
- During 2004–2008, rates of P&S syphilis increased the most among 15–24 year-old men and women.


